Boost Your Speed: Hardware Upgrades to Make Your Computer Faster
Modern systems often slow down due to outdated components and inefficient software. Upgrading key hardware components can significantly improve computer performance and responsiveness. Core elements like the CPU, RAM, and storage play a vital role in how smoothly your device operates.
For example, SSDs offer up to 5-7x faster read/write speeds compared to traditional HDDs. This means quicker boot times and faster file transfers. Additionally, 64-bit systems support much larger amounts of RAM, enabling better multitasking and smoother operation for memory-intensive tasks.
Software tools like MiniTool System Booster can also optimize background processes and system resources. Combining proactive hardware upgrades with regular software maintenance ensures maximum speed gains. Whether you’re an average user or a professional, these strategies can deliver noticeable improvements in your computer’s efficiency.
What Hardware Makes a Computer Run Faster?
The processor is the brain of your system, dictating how quickly tasks are executed. Known as the CPU, it handles billions of instructions per second, making it a critical component for speed and efficiency.
The Role of the Processor (CPU)
Modern CPUs, like the Intel i9-13900K, feature up to 24 cores, enabling them to tackle intensive workloads with ease. Each core can handle multiple tasks simultaneously, improving multitasking and overall processing power.
Technologies like Thermal Velocity Boost automatically increase clock speeds when cooling allows, ensuring peak performance during demanding tasks. Tools like CPU-Z help monitor real-time performance metrics, giving users insights into their system’s capabilities.
How Clock Speed and Cores Affect Performance
Clock speed, measured in GHz, determines how fast a CPU can execute instructions. Higher speeds, like 5.0GHz, result in quicker single-threaded performance, ideal for gaming and everyday tasks.
Meanwhile, additional cores enhance multitasking and parallel processing. For example, a 6-core processor can handle 4K video editing 47% faster than a quad-core model. Overclocking, such as boosting the i7-12700K from 3.6GHz to 5.0GHz, can increase benchmark scores by 31%.
Advanced cooling solutions, like liquid cooling, enable sustained high speeds without thermal throttling, ensuring consistent performance.
Upgrade Your RAM for Multitasking Mastery
Enhancing your system’s multitasking capabilities starts with upgrading your RAM. Random Access Memory (RAM) is crucial for handling multiple applications simultaneously, ensuring smooth operation and responsiveness. Whether you’re gaming, editing videos, or running complex software, having sufficient memory can make a significant difference.
How Much RAM Do You Really Need?
For modern gaming PCs, 16GB of RAM is the minimum requirement. However, content creators and professionals should aim for 32GB to handle memory-intensive tasks like 3D rendering or video editing. High-end productivity builds can even benefit from 64GB kits, which are now more affordable than ever.
Dual-channel configurations can boost performance by up to 22%, especially for tasks that demand high bandwidth. Tools like MemTest86 ensure memory stability before overclocking, while XMP profiles simplify achieving rated speeds with just one click.
DDR3 vs. DDR4 vs. DDR5: Choosing the Right Memory
When selecting RAM, it’s essential to understand the differences between DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5. DDR5-6400 offers 50% more bandwidth than DDR4-3200, making it ideal for future-proofing your system. However, older motherboards may not support DDR5 voltages, so compatibility checks are crucial.
Latency is another factor to consider. While DDR4 CL16 provides lower latency, DDR5 CL40 compensates with higher speeds. For temporary workloads, RAM disk solutions can achieve speeds of up to 15,000MB/s, offering a significant performance boost.
Swap Your Hard Drive for an SSD
Upgrading your storage solution can dramatically transform your system’s performance. Traditional HDDs are reliable but often lag in speed. Switching to an SSD can deliver faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and improved overall responsiveness.

HDD vs. SSD: Speed Differences Explained
HDDs use spinning disks to access data, which limits their speed. In contrast, SSDs rely on flash memory, offering significantly faster read/write speeds. For example, a typical HDD might achieve 120MB/s, while a SATA SSD can reach up to 550MB/s.
This speed difference is especially noticeable during boot-up or when launching applications. SSDs also have no moving parts, making them more durable and less prone to mechanical failure.
NVMe vs. SATA: Which SSD Is Best for You?
When choosing an SSD, you’ll encounter two main types: SATA and NVMe. SATA SSDs are affordable and widely compatible, making them a great choice for general use. However, NVMe SSDs leverage PCIe lanes, achieving speeds up to 7,400MB/s.
For gamers and professionals, NVMe drives like the Samsung 990 Pro offer unparalleled performance. They’re ideal for tasks requiring high-speed data access, such as video editing or 3D rendering.
| Type | Read/Write Speed | Price (1TB) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDD | 120MB/s | $0.02/GB | Cold Storage |
| SATA SSD | 550MB/s | $0.08/GB | General Use |
| NVMe SSD | 7,400MB/s | $0.10/GB | High-Performance Tasks |
Whether you opt for a SATA or NVMe SSD, the upgrade will significantly enhance your system’s speed and efficiency. For those on a budget, SATA SSDs provide a cost-effective solution, while NVMe drives cater to demanding workloads.
Don’t Overlook the Power of Cache Memory
Cache memory plays a critical role in boosting system efficiency. It acts as a high-speed buffer between the processor and RAM, ensuring faster access to frequently used data. This reduces latency and enhances overall performance.
Modern CPUs, like the AMD Ryzen 9 7950X, feature up to 80MB of combined L2 and L3 cache. This large cache size significantly improves multitasking and reduces delays in processing instructions. Cache hit rates above 95% can cut memory latency by 40ns, making operations smoother and more responsive.
Technologies like SmartCache further optimize performance by sharing L3 cache between CPU cores. This ensures efficient resource allocation, especially during intensive tasks like gaming or video editing. For example, game loading times can improve by 15% with processors that have larger cache sizes.
- Cache prefetching algorithms predict data needs, reducing wait times.
- Memory hierarchy (Registers > L1 > L2 > L3 > RAM > Storage) ensures data flows efficiently.
- Specialized cache optimization is crucial for database servers and machine learning tasks.
Whether you’re a gamer, professional, or tech enthusiast, understanding and leveraging cache memory can unlock your system’s full potential. Overclocking cache separately from core clocks can also provide additional speed gains, ensuring peak performance for demanding workloads.
Motherboard Compatibility and Performance
The motherboard serves as the backbone of your system, connecting all critical components. It ensures seamless communication between the CPU, RAM, storage, and other hardware components. Choosing the right motherboard is essential for maximizing power and performance.
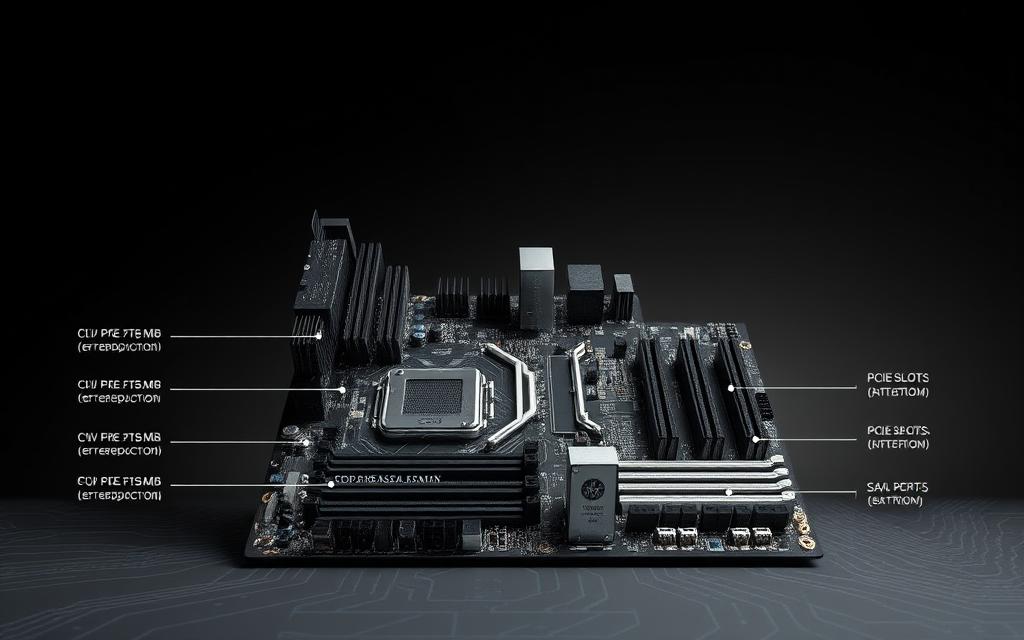

Why Chipset and Expansion Slots Matter
Modern motherboards feature advanced chipsets like the Intel Z790, which supports 13th Gen Intel processors and overclocking. These chipsets enhance power delivery and thermal management, allowing for higher performance. Expansion slots, such as PCIe 5.0 x16, provide up to 32 GT/s per lane, enabling next-gen GPUs and storage devices.
High-quality Voltage Regulator Modules (VRMs) are crucial for stable power delivery. Motherboards with 16+ phase VRM designs ensure efficient power distribution, reducing voltage fluctuations and improving overclocking potential. This is especially important for demanding workloads and high-performance systems.
Thunderbolt 4 support requires specific header connections on the motherboard. These headers enable high-speed data transfer, dual 4K display support, and charging capabilities. Without proper connections, Thunderbolt ports may not function at their full potential.
BIOS flashback is a valuable feature that allows firmware updates without a CPU or memory installed. This is particularly useful when upgrading to newer processors or recovering from failed updates. Simply download the latest BIOS file, place it on a USB drive, and connect it to the designated port.
Multi-GPU configurations need careful PCIe lane distribution to avoid bottlenecks. High-end motherboards provide multiple PCIe x16 slots with sufficient lane allocation, ensuring optimal performance for each GPU. Always check the motherboard’s specifications to confirm compatibility.
M.2 slots with heatsinks prevent thermal throttling in SSDs during intensive operations. Proper cooling maintains consistent performance and extends the lifespan of your storage devices. Some motherboards come with built-in heatsinks, while others may require aftermarket solutions.
USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 offers data transfer speeds of up to 20 Gbps, doubling the bandwidth of previous standards. This is ideal for transferring large files or streaming high-resolution media. Ensure both the host and device support this standard for maximum speed.
POST code displays are diagnostic tools that help troubleshoot hardware issues during the Power-On Self-Test process. These codes indicate problems with the CPU, memory, or other components, streamlining the troubleshooting process for system builders and overclockers.
When choosing a motherboard, consider the form factor. E-ATX boards offer more expansion slots and features, while microATX boards are compact and cost-effective. Your choice depends on your system’s requirements and available space.
Cooling Systems to Prevent Throttling
Efficient cooling is essential for maintaining peak performance in any system. Overheating can cause thermal throttling, reducing the speed and efficiency of your components. Investing in advanced cooling solutions ensures your hardware operates at its best, even under heavy workloads.
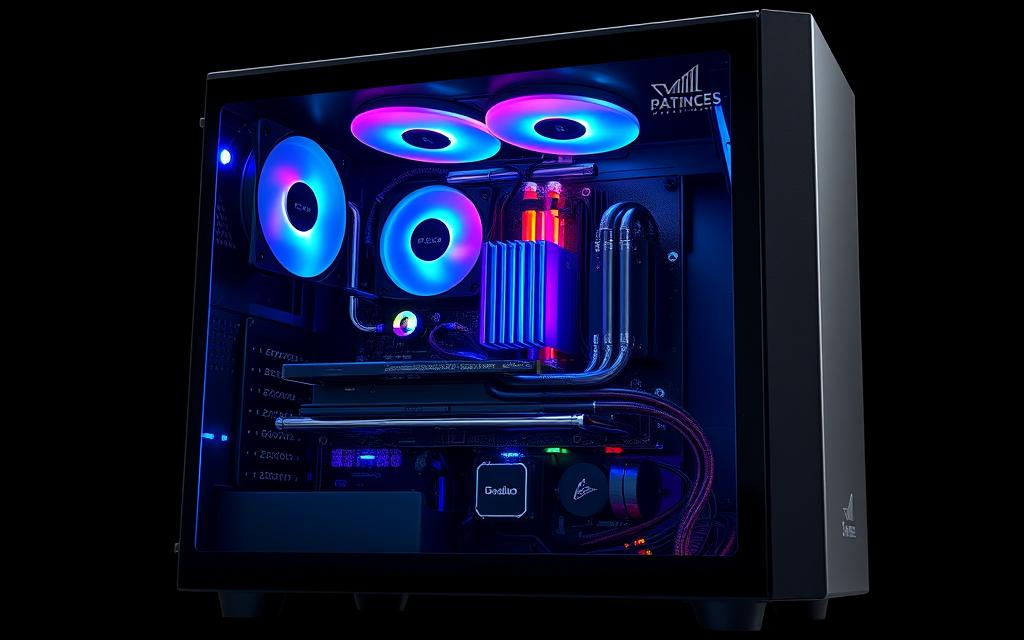

360mm AIO coolers are a popular choice, capable of dissipating over 300W of thermal load. These all-in-one liquid coolers are easy to install and provide excellent heat management. For even better results, thermal compounds like Thermal Grizzly Kryonaut can reduce temperatures by up to 5°C compared to standard pastes.
Optimizing case airflow is another critical factor. Positive pressure configurations prevent dust buildup while maintaining efficient cooling. PWM fans offer a balance between noise and performance, adjusting speeds based on temperature needs.
For extreme overclocking, liquid metal thermal interface materials (TIM) provide superior heat transfer. However, they require careful application to avoid short circuits. GPU deshrouding with aftermarket cooling solutions can also enhance performance, especially for high-end graphics cards.
Undervolting is a practical technique to reduce heat without sacrificing performance. For example, undervolting an RTX 4090 can lower temperatures by 12°C while maintaining full power. Phase-change thermal pads are another innovative solution, improving VRM cooling and stability.
| Cooling Solution | Key Benefit | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 360mm AIO Cooler | Dissipates 300W+ thermal loads | High-performance systems |
| Thermal Grizzly Kryonaut | Reduces temps by 5°C | Overclocking and gaming |
| PWM Fans | Optimal noise/performance balance | General use and multitasking |
| Liquid Metal TIM | Superior heat transfer | Extreme overclocking |
| Undervolting | Reduces temps without performance loss | High-end GPUs and CPUs |
Custom water loops offer the ultimate cooling solution but require regular maintenance. Thermal camera analysis can help identify hotspots, ensuring your system stays cool under pressure. By implementing these strategies, you can prevent throttling and unlock your system’s full potential.
Optimize Performance with Software Tweaks
Fine-tuning your system with software adjustments can unlock hidden performance potential. While hardware upgrades are essential, optimizing your operating system and applications ensures smoother and faster operation. From clearing cache to updating drivers, these tweaks can significantly enhance your system performance.

Clearing Cache and Background Processes
Over time, cached files and unnecessary background processes can slow down your system. Tools like Norton Utilities help clean up system files and improve system performance. Its Startup Manager can reduce boot times by up to 40%, ensuring a faster startup.
For Windows users, disabling Memory Integrity in Windows 11 can recover up to 15% performance lost to security overhead. Additionally, utilities like Autoruns reveal over 300 startup locations, allowing you to disable unnecessary programs. MiniTool System Booster’s ActiveCare feature also auto-optimizes resources, keeping your system running efficiently.
Updating Drivers for Peak Efficiency
Outdated drivers can hinder system performance and cause compatibility issues. Tools like Driver Booster 10 automatically update 98% of your system’s drivers, ensuring peak efficiency. For GPU-specific updates, Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) ensures a clean installation, eliminating potential conflicts.
LatencyMon is another valuable tool for identifying DPC latency issues, which can cause stuttering in Windows systems. Process Lasso allows you to prioritize CPU cores for critical applications, ensuring smoother multitasking. Registry optimizations, such as NTFS performance tuning, further enhance your operating system’s responsiveness.
- Disable telemetry services via Group Policy edits to free up resources.
- Use Process Lasso to manage CPU core allocation for demanding tasks.
- Regularly clear cache and optimize background processes for sustained performance.
Conclusion
Achieving peak system speed requires a strategic approach. Upgrading components like the CPU, RAM, and SSD can deliver 3-8x real-world improvements. Pairing these hardware upgrades with software optimization ensures balanced performance.
Modern technologies like DDR5 and PCIe 5.0 future-proof your setup through 2026. Monitoring tools like HWInfo64 help track the effectiveness of these changes. Allocating your budget wisely—40% GPU, 25% CPU, 20% storage, and 15% cooling—ensures optimal results.
Energy-efficient components reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Recycling programs for old computer parts promote sustainability. Regular maintenance and professional benchmarking keep your system running smoothly for years to come.
FAQ
How does the processor (CPU) impact system performance?
The CPU handles all processing tasks. A faster processor with higher clock speeds and more cores can execute instructions quicker, improving overall speed.
How much RAM is necessary for smooth multitasking?
For basic tasks, 8GB suffices. For gaming or heavy applications, 16GB or more ensures better performance and prevents slowdowns.
What’s the difference between DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 memory?
DDR5 is the latest, offering faster data transfer rates and lower power consumption compared to DDR4 and DDR3, which are older and slower.
Why should I replace my HDD with an SSD?
SSDs provide faster read/write speeds, reducing boot times and improving data access. They’re more reliable and efficient than traditional hard drives.
Which is better: NVMe or SATA SSDs?
NVMe SSDs are faster than SATA SSDs due to their direct connection to the motherboard. However, SATA SSDs are more affordable and still significantly quicker than HDDs.
How does cache memory improve processing speed?
Cache memory stores frequently accessed data, allowing the CPU to retrieve it quickly. Larger cache sizes reduce latency and enhance performance.
Why is motherboard compatibility important?
The motherboard determines which components you can use. A compatible chipset and expansion slots ensure optimal performance and future upgradeability.
How do cooling systems prevent throttling?
Efficient cooling keeps the CPU and GPU temperatures in check, preventing thermal throttling that can slow down performance during intensive tasks.
Can software tweaks improve system speed?
Yes, clearing cache, closing background processes, and updating drivers can free up resources and ensure your system runs at peak efficiency.